Personal finance is not just about how to earn, spend, and save. In its broader context, it involves decision-making to achieve financial stability and planning towards financial freedom. This introduction to personal finance covers managing one’s or one’s family’s financial resources, such as saving, spending, and investing. Understanding the importance of personal finance enables individuals to budget their spending, manage their finances effectively, and ensure their financial health. Ultimately, this helps them accomplish both short-term and long-term financial goals, resulting in greater happiness and life satisfaction. If you’re just starting or have decided to improve your money management skills, learning the basics of personal finance will ensure a more secure future.
Key areas of personal finance include budgeting, saving, investing, debt handling, and planning. All of these play a crucial role in establishing financial balance and providing long-term security. The components of personal finance work together to create a comprehensive approach to managing your money and achieving financial wellbeing.

Contents
Analyze Your Current Financial Situation
The first step towards improving personal financial management is understanding where you stand financially. This includes looking at your total income and spending patterns, debts, and savings. Make a complete list of all your regular expenses like bills, loans, and so on. It also enables you to plug loopholes, since now you know where you are spending your cash most. Understanding your financial landscape involves figuring out financial priorities and anticipating potential financial shocks.
Setting Financial Goals
Creating specific financial goals will help keep you motivated and focused on your financial strategy. You can start with general goals like building an emergency fund for a few months, and for long-term goals, you might aim to create a retirement fund or buy a house, among others. SMART goals (Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, Time-bound) are excellent tools that guide you on your journey toward financial freedom.
Budgeting: Your Financial Roadmap
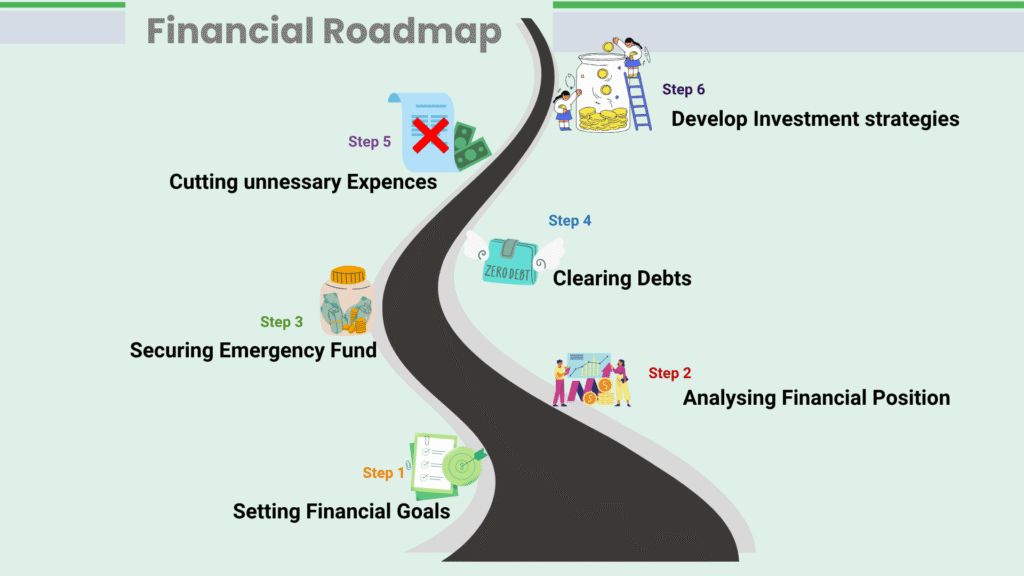
A monthly budget is a critical step in managing your cash flow effectively. Begin by tracking your expenses; prioritize what is necessary and then find ways to reduce discretionary expenditures. Then assign your earned income to cover essential and discretionary expenses, and savings. Follow the simple formula of the 50:30:20 rule: spend half of your earnings on needs, 30% on wants and discretionary spending, and 20% on saving and debt repayment. This monthly budget strategy can really help instill financial discipline and a good savings habit. Learning how to manage money through effective budgeting is a fundamental aspect of personal finance.
Creating an Emergency Fund
Life is full of surprises and financial shocks along the way. An emergency fund can be considered your financial safety net. The emergency fund is simply a cash reserve set aside to cover unexpected expenses or financial emergencies. Strive to save for three to six months’ worth of living costs in a readily accessible savings account.
Arrange for automatic savings transfers from your checking account to your savings or investment account. By doing so, you’ll avoid constantly moving money to your savings manually. Your emergency fund will assist you in catering for mishaps such as loss of income, sickness, or even a house breakdown, without necessarily being forced to abandon your financial plan.
For those curious about how to build an emergency fund, begin by allocating a percentage of your earnings on a regular basis and increasing contributions over time. Emergency fund examples include saving for unforeseen car repairs, medical bills, or a short-term loss of income. Keep your emergency fund in liquid, low-risk assets such as high-yield savings accounts or money market funds..
Effectively Managing Debt
Understanding good debt and bad debt is crucial to successful debt management and setting a stable financial future. Debt can stand in the way of financial freedom, but it can be managed with a good strategy. Prioritize paying off debts with high interest first while only making the minimum payments on other loans. To keep yourself motivated, try the snowball method (paying off the smallest debts first) or the avalanche method (paying off the highest-interest debts first). Debt avoidance should be a key part of your strategy for long-term financial health.
Also, work on building your credit score through good payment habits and responsible credit utilization since this will benefit you in many ways.
Start Investing to Grow Wealth
Saving is the initial step that plays a significant role in wealth formation in the long run. But saving in itself is not enough for building wealth. You’ll need to explore other personal investment opportunities to grow your wealth effectively. Popular investment options include stocks, bonds, unit trusts, exchange-traded funds, and real estate. Additionally, understanding your risk tolerance and implementing diversification in your investment strategy can significantly lower risk while ensuring appropriate returns for long-term growth. The earlier you start investing, the better your chances of benefiting from compound interest.
Risk management is a critical part of investing. By diversifying your portfolio and understanding your risk tolerance, you can protect your investments against market fluctuations and economic shocks. Wealth management strategies often incorporate a mix of different investment types to balance risk and potential returns.
Planning for Retirement
Even though retirement may feel far away, it’s essential to include it in your financial planning now. Starting early with retirement planning significantly improves your financial outlook due to the power of compound interest. Contribute to various retirement plans, including National Pension Schemes (NPS), Provident Funds, and other pension plans. To kick-start retirement planning, periodically calculate how much money you’ll need and increase your contributions accordingly. Take advantage of employer matching programs and consider consulting a financial advisor to help you meet your retirement goals. Financial planning for beginners should always include a focus on long-term retirement savings.
Protecting Your Financial Future
Insurance is a vital part of personal finance that covers your assets and livelihood. Health insurance, life insurance, disability insurance, and property insurance in particular can save you and your family from hardship. Insurance for a person should be analyzed based on their situation and financial status, then buy those which provide adequate protection. When choosing the insurance company and policy, it is important to consider coverage limits, deductibles, and the insurance company’s reputation. The right insurance coverage is an essential component of a comprehensive financial strategy.
Effective Tax Planning
For the optimization of personal wealth, the process of tax planning is crucial. Understanding tax principles can have a powerful impact on your overall financial situation. Some traditional tax-saving strategies include tax-sheltered plans and various kinds of deductions. It is a good idea to understand tax brackets so you can make appropriate decisions. Finally, consider implementing advanced tax planning strategies beyond the tax season to develop better outcomes during the tax season. Seeking financial advice from a tax professional can help you navigate complex tax situations and maximize your savings.
Keep Learning and Growing Financially
The world of personal finance is ever-evolving. Stay informed by reading books, attending seminars, tuning into finance-related blogs, podcasts, and taking courses. Stay up-to-date on changes in laws and trends, and consult financial professionals when necessary. Keep educating yourself to the point where you can make well-informed decisions based on shifts in the financial industry. Improving your financial literacy through personal finance education is an ongoing process that will benefit you throughout your life.
Conclusion
Learning how to manage personal finances is an ongoing journey requiring constant education and adjustment. Taking the initiative to understand your financial health, setting goals, and developing plans strengthens your path to financial independence. Budgeting, saving, investing, and retirement planning may seem distant at times, but they are all essential to building a stable financial future. By securing insurance and employing effective tax strategies, you ensure your financial security and build a legacy of wealth.
Ongoing learning and staying updated on financial trends help you to make smart decisions. The sooner you act, the sooner you’ll be in a better position. Before long, you’ll enjoy a new path of stability with exponential growth in every direction, no longer burdened by money concerns.
Remember, an essential part of managing personal finances is being prepared for emergencies. If you’re in a position where you need emergency money, having a well-funded emergency fund will be your safety net. If you’re one of those thinking, “I need emergency money,” start building your fund today to avoid future financial stress. For those wondering how to get emergency money quickly, having a robust emergency fund is the best solution.
Why wait until tomorrow? Your future self will thank you for the financial stability and security that you create through regular savings and sound financial planning. With these principles and having an adequately funded emergency account, you will be equipped to withstand any financial shock that life may have in store for you, securing your long-term financial health.
By implementing the best financial planning practices and utilizing various financial planning tools, you can take control of your financial future. Whether you’re just starting or looking to refine your approach, remember that personal finance is a journey of continuous improvement and adaptation to your changing life circumstances and financial goals.



Incredible